Home» About Our Cooking Classes» Classes – By Category
Classes – By Category
Come cook with us!
Scroll down for a list of our current cooking classes, listed by culinary categories. Or click the buttons below to download a printer-friendly version of the class list or to view the class calendar.
CHOOSE ANOTHER CATEGORY >>
The Ultimate Cheat Sheet for Understanding Porter's Five Forces Model
Porter's Five Forces Model is a strategic framework that helps businesses analyze the competitive forces in their industry and make informed decisions. It was developed by Michael Porter, a renowned professor at Harvard Business School, and has become one of the most widely used tools in strategic management. Understanding this model is crucial for businesses as it provides valuable insights into the dynamics of their industry and helps them develop effective strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
What is Porter's Five Forces Model?
Porter's Five Forces Template is a framework that analyzes the competitive forces in an industry to determine its attractiveness and profitability. The model consists of five forces: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitutes, and competitive rivalry. By understanding these forces and their interactions, businesses can identify opportunities and threats in their industry and develop strategies to mitigate risks and gain a competitive advantage.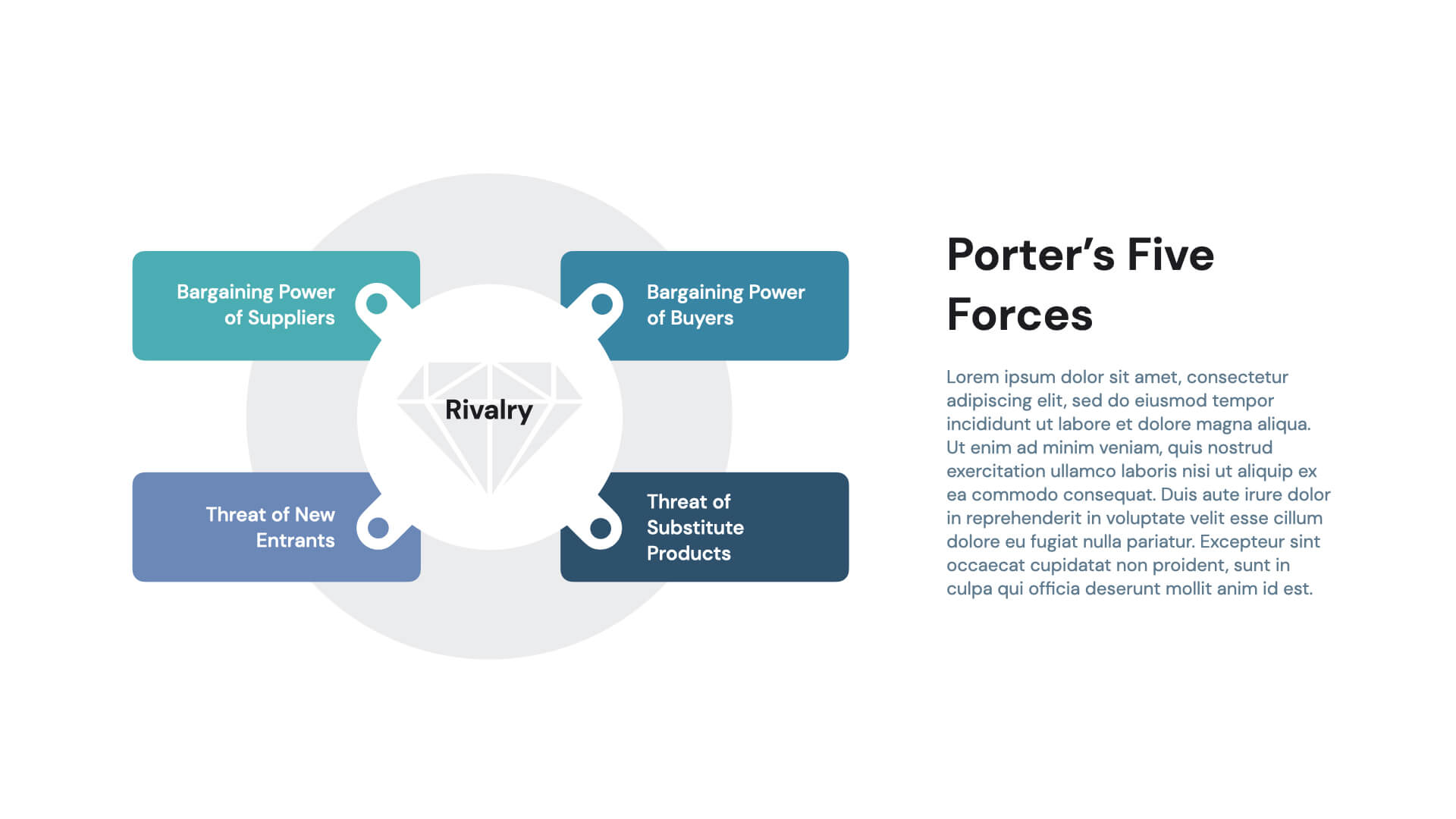
The model was first introduced by Michael Porter in his book "Competitive Strategy" in 1979. Porter argued that understanding the competitive forces in an industry is essential for businesses to develop effective strategies. He believed that the intensity of these forces determines the potential for profit in an industry. By analyzing these forces, businesses can identify areas where they have a competitive advantage and focus their resources on those areas.
The Importance of Understanding Porter's Five Forces Model
Understanding Porter's Five Forces Model has several benefits for businesses. Firstly, it helps them gain a deeper understanding of their industry and the dynamics that shape it. By analyzing the five forces, businesses can identify the key drivers of competition in their industry and develop strategies to address them.
Secondly, the model helps businesses make informed strategic decisions. By understanding the forces at play in their industry, businesses can identify opportunities for growth and develop strategies to exploit them. For example, if the threat of new entrants is low, a business may choose to invest in expanding its market share. On the other hand, if the threat of substitutes is high, a business may focus on developing unique products or services to differentiate itself from competitors.
Several successful companies have used Porter's Five Forces Model to gain a competitive advantage. For example, Apple used the model to identify the threat of substitutes in the smartphone industry and developed a unique product, the iPhone, that revolutionized the market. Similarly, Amazon used the model to identify the bargaining power of suppliers in the retail industry and developed a robust supply chain that allowed it to offer competitive prices and fast delivery.
The Five Forces: A Brief Overview
The five forces in Porter's Five Forces Model are:
1. Threat of New Entrants: This force measures the ease with which new competitors can enter an industry. Factors that affect the threat of new entrants include barriers to entry, economies of scale, and government regulations.
2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers: This force measures the power that suppliers have over businesses in an industry. Factors that affect the bargaining power of suppliers include the number of suppliers, the uniqueness of their products or services, and their ability to switch suppliers.
3. Bargaining Power of Buyers: This force measures the power that buyers have over businesses in an industry. Factors that affect the bargaining power of buyers include the number of buyers, their ability to switch suppliers, and their price sensitivity.
4. Threat of Substitutes: This force measures the likelihood that customers will switch to alternative products or services. Factors that affect the threat of substitutes include price-performance trade-offs, switching costs, and customer loyalty.
5. Competitive Rivalry: This force measures the intensity of competition among existing players in an industry. Factors that affect competitive rivalry include the number and size of competitors, industry growth rate, and product differentiation.
It is important for businesses to consider all five forces when analyzing their industry as they are interconnected and influence each other. For example, a high threat of new entrants may increase competitive rivalry and reduce the bargaining power of suppliers. By considering all five forces, businesses can develop a comprehensive understanding of their industry and make informed strategic decisions.
The First Force: Threat of New Entrants
The threat of new entrants is the first force in Porter's Five Forces Model https://hislide.io/blog/porters-five-forces-analysis-is-an-effective-tool-for-your-business/. It measures the ease with which new competitors can enter an industry and compete with existing players. Factors that affect the threat of new entrants include barriers to entry, economies of scale, and government regulations.
Industries with high barriers to entry, such as the airline industry or the pharmaceutical industry, have a low threat of new entrants. These barriers can include high capital requirements, patents or copyrights, and government regulations. On the other hand, industries with low barriers to entry, such as the restaurant industry or the retail industry, have a high threat of new entrants. In these industries, it is relatively easy for new competitors to enter the market and compete with existing players.
Understanding the threat of new entrants is crucial for businesses as it helps them assess the potential for new competition in their industry. By analyzing this force, businesses can identify areas where they have a competitive advantage and develop strategies to protect their market share. For example, they may invest in building strong brand loyalty or developing unique products or services that are difficult to replicate.
The Second Force: Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is the second force in Porter's Five Forces Model. It measures the power that suppliers have over businesses in an industry. Factors that affect the bargaining power of suppliers include the number of suppliers, the uniqueness of their products or services, and their ability to switch suppliers.
Industries with few suppliers or a limited number of alternative suppliers have a high bargaining power of suppliers. In these industries, suppliers can dictate terms to businesses and charge higher prices. On the other hand, industries with many suppliers or a wide range of alternative suppliers have a low bargaining power of suppliers. In these industries, businesses have more options and can negotiate better terms with suppliers.
Understanding the bargaining power of suppliers is important for businesses as it helps them assess the potential impact of supplier relationships on their profitability. By analyzing this force, businesses can identify areas where they may face challenges in sourcing inputs or negotiating favorable terms with suppliers. They can then develop strategies to mitigate these risks, such as diversifying their supplier base or building long-term partnerships with key suppliers.
The Third Force: Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of buyers is the third force in Porter's Five Forces Model. It measures the power that buyers have over businesses in an industry. Factors that affect the bargaining power of buyers include the number of buyers, their ability to switch suppliers, and their price sensitivity.
Industries with few buyers or a limited number of alternative products or services have a high bargaining power of buyers. In these industries, buyers can demand lower prices or better terms from businesses. On the other hand, industries with many buyers or a wide range of alternative products or services have a low bargaining power of buyers. In these industries, businesses have more options and can charge higher prices.
Understanding the bargaining power of buyers is important for businesses as it helps them assess the potential impact of customer relationships on their profitability. By analyzing this force, businesses can identify areas where they may face challenges in attracting and retaining customers. They can then develop strategies to mitigate these risks, such as offering unique products or services or providing exceptional customer service.
The Fourth Force: Threat of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes is the fourth force in Porter's Five Forces Model. It measures the likelihood that customers will switch to alternative products or services. Factors that affect the threat of substitutes include price-performance trade-offs, switching costs, and customer loyalty.
Industries with many substitutes or a wide range of alternative products or services have a high threat of substitutes. In these industries, customers have more options and can easily switch to a substitute if they find it more attractive. On the other hand, industries with few substitutes or a limited number of alternative products or services have a low threat of substitutes. In these industries, customers have fewer options and are less likely to switch.
Understanding the threat of substitutes is important for businesses as it helps them assess the potential impact of alternative products or services on their profitability. By analyzing this force, businesses can identify areas where they may face challenges in attracting and retaining customers. They can then develop strategies to mitigate these risks, such as offering unique features or benefits that are not available in substitutes.
The Fifth Force: Competitive Rivalry
Competitive rivalry is the fifth force in Porter's Five Forces Model. It measures the intensity of competition among existing players in an industry. Factors that affect competitive rivalry include the number and size of competitors, industry growth rate, and product differentiation.
Industries with many competitors or a high concentration of market share have a high competitive rivalry. In these industries, businesses compete fiercely for market share and profitability is often low. On the other hand, industries with few competitors or a low concentration of market share have a low competitive rivalry. In these industries, businesses have more pricing power and profitability is often high.
Understanding competitive rivalry is important for businesses as it helps them assess the potential impact of competition on their profitability. By analyzing this force, businesses can identify areas where they may face challenges in gaining market share or maintaining profitability. They can then develop strategies to mitigate these risks, such as focusing on niche markets or differentiating their products or services.
How to Apply Porter's Five Forces Model to Your Business
Applying Porter's Five Forces Model to your business involves a step-by-step process:
1. Identify the industry: Start by identifying the industry in which your business operates. This could be a broad industry, such as the automotive industry, or a specific niche within an industry, such as electric vehicles.
2. Define the boundaries: Define the boundaries of your industry by identifying the key players and products or services that compete in the market. This will help you focus your analysis on the relevant forces.
3. Analyze each force: Analyze each of the five forces in your industry by considering the factors that affect them. For example, when analyzing the threat of new entrants, consider barriers to entry, economies of scale, and government regulations.
4. Assess the intensity: Assess the intensity of each force by considering its impact on your business. For example, if the threat of new entrants is high, consider how this could affect your market share and profitability.
5. Develop strategies: Develop strategies to address each force based on your analysis. For example, if the threat of new entrants is high, consider investing in building strong brand loyalty or developing unique products or services.
Tips for using Porter's Five Forces Model effectively:
- Involve key stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the analysis process to gain different perspectives and insights.
- Update regularly: Regularly update your analysis to reflect changes in your industry and adapt your strategies accordingly.
- Consider external factors: Consider external factors, such as technological advancements or changes in customer preferences, that may impact the forces in your industry.
Examples of businesses that have successfully used Porter's Five Forces Model:
- Apple: Apple used Porter's Five Forces Model to identify the threat of substitutes in the smartphone industry and developed a unique product, the iPhone, that revolutionized the market.
- Amazon: Amazon used Porter's Five Forces Model to identify the bargaining power of suppliers in the retail industry and developed a robust supply chain that allowed it to offer competitive prices and fast delivery.
Limitations of Porter's Five Forces Model and How to Overcome Them
While Porter's Five Forces Model is a valuable tool for analyzing industry dynamics, it has some limitations:
- Limited scope: The model focuses on the external factors that shape an industry and does not consider internal factors, such as a company's resources or capabilities.
- Static analysis: The model provides a snapshot of industry dynamics at a specific point in time and does not account for changes over time.
- Lack of quantitative analysis: The model does not provide a quantitative analysis of the forces and relies on subjective judgments.
To overcome these limitations, businesses can:
- Use other strategic frameworks: Use other strategic frameworks, such as SWOT analysis or PESTEL analysis, to complement Porter's Five Forces Model and gain a more comprehensive understanding of their industry.
- Conduct primary research: Conduct primary research, such as surveys or interviews, to gather quantitative data on the forces in your industry.
- Update regularly: Regularly update your analysis to reflect changes in your industry and adapt your strategies accordingly.
Examples of businesses that have overcome the limitations of Porter's Five Forces Model:
- Google: Google uses a combination of Porter's Five Forces Model and other strategic frameworks to analyze the dynamics of the search engine industry and develop strategies to maintain its market dominance.
- Tesla: Tesla uses a combination of Porter's Five Forces Model and other strategic frameworks to analyze the dynamics of the electric vehicle industry and develop strategies to differentiate itself from competitors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Porter's Five Forces Model is crucial for businesses as it provides valuable insights into the competitive forces in their industry and helps them develop effective strategies. By analyzing the five forces, businesses can identify opportunities and threats in their industry and make informed strategic decisions. While the model has some limitations, businesses can overcome them by using other strategic frameworks, conducting primary research, and updating their analysis regularly. Overall, Porter's Five Forces Model is a powerful tool that can help businesses gain a competitive advantage and achieve long-term success.
